Grease Recycling: Unlock Maximum Benefits for Your Business
Commercial kitchens nationwide generate thousands of gallons of used cooking oil (UCO) and fats, oils, and grease (FOG) each year. This presents disposal challenges, compliance risks, and missed sustainability opportunities. This guide to the grease recycling process offers a clear roadmap for transforming UCO into biodiesel, preventing sewer blockages, and cutting waste management costs. We also cover specialized dumpster rental solutions designed for enterprises with 50 to 5,000 locations. In this article, you’ll learn:
- A detailed look at commercial grease recycling, including the role of grease traps and interceptors.
- The environmental and economic advantages, from reducing your carbon footprint to creating new revenue streams.
- Best practices for regulatory compliance and maintenance to keep your operations efficient.
- Enterprise-level strategies for collecting UCO across multiple locations, managing industrial waste oil , and consolidating reporting.
- Answers to common questions about grease recycling, profitability, and trap maintenance.
By following this guide, you’ll gain a comprehensive understanding of the grease recycling process, its importance for sustainability and cost control, and how National Waste’s dumpster rental services provide a complete solution for large-scale food service operations.
What is Commercial Grease Recycling and How Does It Work?
The commercial grease recycling process converts spent cooking oil and trap waste into valuable renewable products through a cycle of collection, separation, processing, and distribution. This systematic approach prevents environmental hazards, generates feedstock for biodiesel, and supports corporate sustainability goals by diverting FOG away from sewers and landfills. Understanding each stage reveals how specialized equipment, logistics, and container rentals work together to optimize business performance and regulatory compliance.
What Are the Key Steps in Recycling Used Cooking Oil (UCO)?
The essential steps in UCO recycling include collection, pretreatment, filtration, conversion, and distribution .
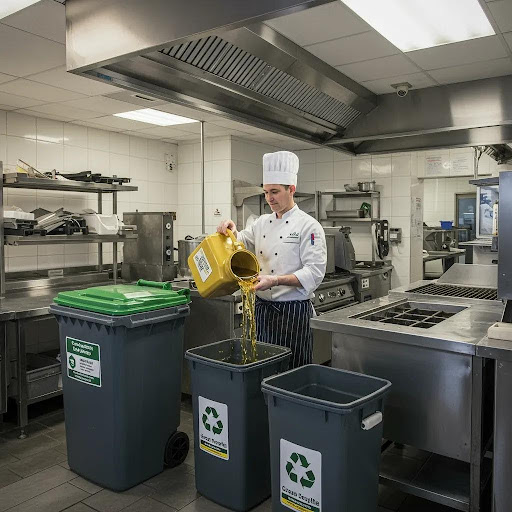
- Collection – Certified haulers collect stored oil from kitchens using sealed containers and roll-off dumpsters.
- Pretreatment – Incoming UCO is first screened to remove solids and food debris.
- Filtration – Finer mesh filters then remove remaining suspended particles to meet processing standards.
- Conversion – The refined oil is processed through transesterification, producing biodiesel and glycerin byproducts.
- Distribution – The resulting biodiesel is certified, blended, and sent to fuel markets, while glycerin is utilized in industrial and agricultural applications.
These steps ensure businesses maximize the value of their UCO while maintaining efficient and compliant operations. Understanding container needs naturally leads to how grease traps and interceptors support the initial collection phase.
How Do Grease Traps and Interceptors Facilitate FOG Collection?
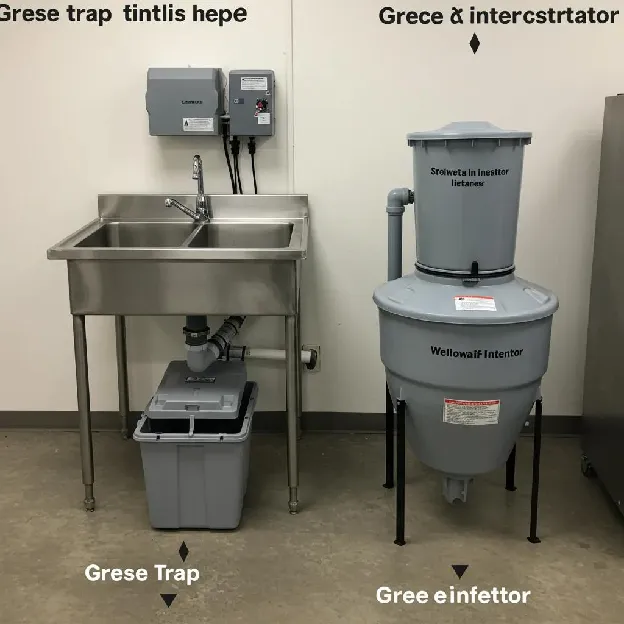

Grease traps and interceptors are onsite separation devices that capture fats, oils, and grease before wastewater enters sewer lines. The table below outlines their core functions and recommended maintenance schedules :
| Device | Separation Mechanism | Typical Capacity | Recommended Cleaning Interval |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grease Trap | Gravity separation within an under-sink unit | 20–100 gallons | Monthly to quarterly |
| Grease Interceptor | Large-scale flow control and retention | 500–2,000 gallons | Quarterly to semi-annually |
Both devices effectively capture FOG, but interceptors are designed for higher volumes and are suitable for multi-unit facilities. Proper maintenance of these separators is crucial for preventing sewer blockages and streamlining the FOG collection stage of the grease recycling process.
What Happens to Collected Grease After Pickup?
Once FOG enters the recycling network, it’s consolidated at regional depots where moisture is removed and the oil is stabilized. Next, advanced biorefineries convert the refined oil into biodiesel through a chemical reaction that replaces glycerin molecules with alcohol-based catalysts. The resulting biodiesel meets ASTM fuel standards, significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions—up to 94 percent less than petroleum diesel. The glycerin byproducts are then used in animal feed, cosmetics, and industrial lubricants, completing the cycle of sustainable waste management.
The chemical process of converting fats and oils into biodiesel is known as transesterification, a reaction that has been extensively studied for its technical aspects and efficiency.
Technical Aspects of Biodiesel Production via Transesterification The process of transesterification is a chemical reaction that converts triglycerides and alcohol into fatty acid alkyl esters (biodiesel) and glycerol. This review covers the technical aspects of biodiesel production by transesterification, including different combinations of oil and catalysts, and the technical tools and processes for monitoring the transesterification.Technical aspects of biodiesel production by transesterification—a review, LC Meher, 2006
How Does Dumpster Rental Support Efficient Grease Recycling?
Dumpster rental services provide dedicated containers specifically sized for UCO drums, grease trap waste, and large FOG volumes, enabling businesses to: maximize grease trap profits .
- Ensure Separation by using designated dumpsters exclusively for grease trap waste.
- Optimize Logistics with scheduled swaps that integrate seamlessly with kitchen operations and prevent overflows.
- Maintain Compliance through documented pickup records and weight tracking.
National Waste’s fleet of roll-off dumpsters and compact grease trap bins work in conjunction with local haulers, offering a single point of contact and unified invoicing for businesses operating at scale. Customized rental schedules reduce manual handling and support a consistent process flow from trap to biorefinery .
What Are the Environmental and Economic Benefits of Commercial Grease Recycling?
Grease recycling offers both environmental and financial advantages by diverting hazardous FOG from sewage systems and producing renewable fuel feedstock. Companies that implement UCO recycling enhance their sustainability profiles, avoid costly fines, and open up new revenue streams—all while lowering disposal expenses and promoting circular economy principles.
How Does Grease Recycling Reduce Carbon Footprint and Sewer Blockages?
By capturing and converting UCO into biodiesel, businesses replace fossil fuels with a low-carbon alternative, cutting greenhouse gas emissions by an average of 60–90 percent. Simultaneously, proper grease trap maintenance and recycling prevent solidified FOG from clogging sewer pipes, thereby avoiding blockages that lead to costly repairs and environmental contamination incidents .
What Are the Cost Savings and Revenue Opportunities for Businesses?
Companies can achieve significant savings through reduced disposal fees and less frequent plumbing maintenance, while also generating revenue by selling their UCO to recycling partners. Typical financial benefits include: saving money through various initiatives.
- Annual disposal cost reductions of 20–40 percent through consolidated dumpster rental and scheduled pickups.
- Revenue generation of $0.10–$0.30 per gallon of UCO sold for biodiesel production.
- Avoidance of fines, which can reach up to $1,000 per incident, for sewer overflows or non-compliance.
These figures demonstrate how integrating grease recycling with dedicated container rental maximizes both cost savings and additional income streams.
How Does Grease Recycling Support Corporate Sustainability and ESG Goals?
Incorporating grease recycling into environmental, social, and governance (ESG) frameworks showcases proactive waste management and aligns with stakeholder expectations. Recycling targets and carbon reduction metrics achieved through UCO diversion contribute to sustainability reporting, green certifications, and investor relations. Tracking container usage and pickup frequencies via centralized dashboards further enhances transparency and accountability across multi-site operations .
Why Is Biodiesel Production from Used Cooking Oil Important?
Biodiesel produced from recycled grease offers a renewable, biodegradable alternative for heavy-duty transport, fleet vehicles, and industrial machinery. Its compatibility with existing diesel engines, coupled with lower particulate emissions and improved lubricity, positions biodiesel as a key element in decarbonizing commercial transportation. This shift towards renewable energy reduces reliance on petroleum markets and ensures supply resilience for large enterprises committed to sustainable fuel sourcing.
The efficiency and yield of biodiesel production are significantly influenced by various factors, including the type of alcohol used, reaction duration, and temperature, with ongoing research exploring new methods like the Biox co-solvent process.
Review of Catalyzed Transesterification for Biodiesel Production The main factors affecting the yield of biodiesel, such as alcohol quantity, reaction time, and reaction temperature, have been discussed. New processes of biodiesel production are also explored, including the Biox co-solvent process which converts used cooking oil into biodiesel.A review on biodiesel production using catalyzed transesterification, DYC Leung, 2010
How Does Grease Trap Cleaning and Maintenance Ensure Compliance and Efficiency?
Regular cleaning of grease traps and interceptors ensures optimal performance, prevents system failures, and meets regulatory requirements. A consistent maintenance schedule combined with proper disposal solutions keeps businesses running smoothly and avoids costly environmental violations.
What Is a Grease Trap and How Does It Differ from a Grease Interceptor?
A grease trap is an under-sink device designed to slow wastewater flow and separate FOG from water using baffles, while a grease interceptor serves larger flows in exterior vaults or floor pits. The following comparison highlights their primary differences :
| Device Type | Installation Location | Flow Capacity | Inspection Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grease Trap | Under-sink | Up to 100 GPM | Monthly |
| Grease Interceptor | Below ground or floor | 100–2,000 GPM | Quarterly |
Choosing the right separator depends on your service volume and kitchen layout , forming the foundation for an effective cleaning regimen.
How Often Should Commercial Grease Traps Be Cleaned?
Commercial grease traps need cleaning when FOG accumulates to 25 percent of the trap’s internal volume, or on a fixed schedule of one to three months, whichever comes first. Adhering to this interval prevents sediment buildup, maintains hydraulic capacity, and mitigates unpleasant odors, ensuring that upstream processes in the grease recycling chain operate without interruption.
What Are the Regulatory Requirements for FOG Management?
FOG management regulations vary by location but typically include: FOG profits your business .
- Mandatory grease trap installation for food service establishments.
- Specific cleaning frequencies based on trap size and usage intensity.
- Requirements for reporting disposal records and manifest tracking.
- Penalties for sewer blockages, improper disposal, or failure to maintain equipment.
Staying informed about federal, state, and local ordinances protects your operations from fines and ensures waste handling aligns with environmental protection standards .
How Does National Waste’s Dumpster Rental Facilitate Grease Trap Waste Disposal?
National Waste’s specialized dumpster rental service provides grease-proof containers with sealable lids and integrated drain ports, allowing for efficient pump-out and transport of trap waste. Each rental includes scheduled pickups synchronized with cleaning cycles, comprehensive manifest documentation, and real-time reporting—combining regulatory compliance with streamlined logistics for multi-location enterprises .
What Are the Best Practices for Used Cooking Oil Collection Services Across Multiple Locations?
Optimizing UCO collection across dozens or thousands of sites requires consistent container standards, coordinated scheduling, and centralized account management. Best practices minimize handling risks, preserve oil quality, and leverage volume discounts to enhance service value for large-scale operators .
How Does National Waste Manage UCO Collection for Businesses with 50 to 5,000 Locations?
National Waste utilizes a national network of vetted haulers under a single contract, ensuring uniform container specifications, synchronized pickup schedules, and consolidated invoices. This approach simplifies procurement, standardizes service levels, and provides a single point of contact—allowing procurement teams to focus on core business operations instead of logistics .
What Storage Solutions Are Recommended for Used Cooking Oil?
Maintaining UCO quality requires durable, sealable containers with vented caps and corrosion-resistant materials. Recommended options include:
- Heavy-duty drum barrels equipped with bungs for air release.
- Intermediate bulk containers (IBCs) with integrated valves for easy draining.
- Portable grease cans on casters for convenient transport.
Proper storage prevents contamination, preserves oil value, and simplifies transfer into roll-off dumpsters for scheduled recycling pickups .
How Does Scheduled Pickup Improve Operational Efficiency?
Scheduled UCO pickups reduce manual coordination efforts, prevent overflow risks, and stabilize inventory levels for kitchens. By aligning service windows with periods of low activity, businesses minimize disruptions and ensure that fryer stations remain clear of full containers—supporting uninterrupted food production and safety .
What Are the Benefits of Professional UCO Collection Services?
Outsourcing UCO collection ensures expert handling, hazard mitigation, and regulatory assurance. Key advantages include: waste minimization .
- Certified Handling that meets all environmental and safety standards.
- Volume Leverage for competitive pricing on container rental and transportation.
- Quality Control through filtration protocols that protect biodiesel yield.
- Centralized Oversight via digital dashboards tracking pickup history and volumes.
These benefits elevate grease recycling from a routine compliance task to a strategic sustainability initiative.
How Do Industrial Waste Oil Recycling and Specialized Dumpster Rentals Support Sustainable Waste Management?
Industrial grease streams, such as machining oils, coolant emulsions, and heavy lubricants, require specialized disposal solutions to protect workers, equipment, and water systems. Recycling these streams conserves valuable feedstocks and prevents hazardous exposures.
What Types of Industrial Waste Oil Require Specialized Disposal?
Common categories of industrial waste oil include:
- Used cutter oils contaminated with metal fines.
- Coolant emulsions blended with chemicals and biocides.
- Hydraulic fluids mixed with particulate matter.
- Dielectric fluids used in high-voltage equipment.
Each type of stream demands specific handling, storage, and transport protocols to comply with hazardous waste regulations .
What Are the Compliance Regulations for Industrial FOG Disposal?
Industrial FOG disposal is regulated under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) and state-level hazardous waste rules, which mandate: FOG profits your business .
- Permitted storage areas with secondary containment.
- Waste characterization and manifest documentation.
- Transport by licensed hazardous waste haulers.
- Reporting of disposal volumes and waste codes.
Adherence to these regulations safeguards corporate liability and environmental integrity .
How Do Specialized Dumpsters Enhance Industrial Waste Oil Management?
Specialized dumpsters for industrial oil feature reinforced, sealed bodies and locking lids to contain spills and odors. Equipped with drip pans and forklift pockets, they facilitate faster loading and unloading while minimizing manual contact. When integrated with scheduled maintenance programs, these dumpsters support continuous production lines and reduce downtime associated with onsite fluid changes. waste .
What Safe Disposal Methods Are Used for Industrial Grease?
Professional facilities utilize thermal desorption, onsite filtration, and solvent extraction to recover base oils and eliminate contaminants. Recovered oils are reprocessed into lubricants or fuel, while residual solids undergo stabilization before safe landfill disposal. These methods maximize resource recovery and ensure compliance with environmental health standards.
The economic viability of biodiesel production can be significantly improved by optimizing the transesterification process and efficiently recovering valuable by-products like glycerol.
Biodiesel Production: A Comprehensive Review of Processes and Economics The continuous transesterification process and the recovery of high-quality glycerol from the biodiesel by-product are primary options to be considered to lower the cost of biodiesel. This review discusses various aspects of biodiesel production, including feedstocks, processes, and challenges.Biodiesel production: a review, Unknown Author, 1999
How Can Multi-Location Businesses Streamline Waste Management with Consolidated Grease Recycling Solutions?
Large enterprises face unique challenges in synchronizing waste streams across diverse sites, reconciling invoices, and ensuring consistent service quality. Consolidated grease recycling solutions simplify these complexities through standardized processes , centralized reporting, and scalable rental plans.
What Challenges Do Large Enterprises Face in Managing Grease Waste?
Enterprises often struggle with inconsistent container types, varied pickup schedules, multiple vendor contacts, and disparate invoicing formats. These issues lead to increased administrative overhead, missed pickups, and compliance gaps that can result in fines or operational delays—hindering supply chain efficiency and sustainability goals .
How Does National Waste Provide Integrated Dumpster Rental and Recycling Services?
National Waste offers a unified solution by coordinating roll-off dumpsters, grease trap bins, and UCO drum exchanges under a single contract. Each site receives standardized containers, synchronized service frequencies, and a single monthly invoice. This integration reduces vendor management complexity and secures consistent pricing, enabling enterprises to accurately forecast waste costs across all locations .
How Does Centralized Reporting Improve Compliance and Cost Control?
Centralized reporting platforms consolidate pickup data, container inventories, and disposal weights into customizable dashboards. Procurement and sustainability teams gain real-time insights into usage trends, compliance status, and recycling outcomes —facilitating informed decision-making and streamlined audit support without manual data compilation.
What Are the Advantages of National Waste’s Scalable Solutions for Multi-Site Operations?
Scalable dumpster rental plans accommodate seasonal volume fluctuations, new site onboarding, and emergency needs without requiring contract renegotiations. Tiered pricing structures offer discounted rates for higher volumes, while dedicated account managers ensure service continuity and rapid responses to operational changes—empowering enterprises to expand their waste programs seamlessly.
What Are the Most Common Questions About Grease Recycling and How Are They Answered?
This section addresses key inquiries regarding process mechanics, eligibility, profitability, and maintenance indicators, providing concise, actionable insights for decision-makers evaluating grease recycling for their operations.
How Is Grease Recycled into Biodiesel and Other Products?
Grease undergoes pretreatment and filtration before entering a reactor where alcohol and catalysts convert triglycerides into biodiesel (fatty acid methyl esters) and glycerin. The biodiesel is then purified and tested to meet fuel standards, while glycerin is refined for use in animal feed, cosmetics, and industrial lubricants—transforming waste into multiple revenue-generating streams .
Can Grease Be Recycled Through Regular Waste Streams?
No, FOG cannot be included in regular recycling or landfill streams due to the significant risk of sewer blockages and contamination. Grease recycling requires dedicated containers, licensed collection, and specialized processing facilities to ensure safe handling and environmental protection.
Who Collects Used Cooking Oil and How Often?
Licensed waste management providers collect UCO from food service establishments on schedules ranging from weekly to quarterly, depending on volume and storage capacity. National Waste coordinates pickups through its network of vetted haulers, aligning service frequency with each site’s consumption and storage capabilities.
Is Grease Recycling Profitable for Commercial Kitchens?
Yes, grease recycling offers profitability through avoided disposal fees, revenue from UCO sales, and reduced maintenance costs. When combined with efficient dumpster rental and centralized logistics, businesses often see a positive return on investment within months of implementing the program.
What Are the Signs That a Grease Trap Needs Cleaning?
Indicators that a grease trap requires service include persistent odors, slow-draining sinks, a visible grease layer exceeding 25 percent of the trap’s volume, and recurring sewer backups. Addressing these signs promptly prevents operational disruptions and supports the continuous flow of the recycling process .
Grease recycling transforms waste liabilities into strategic assets—enhancing sustainability, driving cost savings, and ensuring regulatory compliance through an integrated process supported by specialized dumpster rental solutions. By adopting a systematic approach, from trap maintenance to biodiesel production, businesses of all sizes can optimize their waste management programs, strengthen their ESG credentials, and unlock new revenue opportunities in today’s green economy.



